Raspi-Node Guide 🍓

Why this guide?
This guide is intended for people who wants to get a Raspberry-pi 4 with full desktop Raspberry Pi OS installed along with all the required software to get a Cardano Node up and running on the blockchain. This can be a nice setup for those seeking to just do some lightweight develerpment on the blockchain like making NFTs for example.
caution
You'll need a monitor (at least for initial setup as SSH is disabled and ufw is up) and you must use the Raspberry Pi 4 with 8GB of RAM!
Download & Flash
Install Raspi-Imager
Download, install & open Raspberry Pi Imager. Plug in your target USB drive.
64 bit Raspberry Pi OS desktop
There is now a 64bit image you can install, it is not available in raspi-imager selection, IDK why. Check out the images in the link below grab the latest version. It is a zip file so we have to unzip it before flashing.
Download Raspberry Pi OS arm64
Unzip the img file and flash it with Raspi-imager. Plug it into your Raspberry Pi 4 and go through the initial setup. Default username=pi and the password=raspberrypi
You can find documentation here https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/
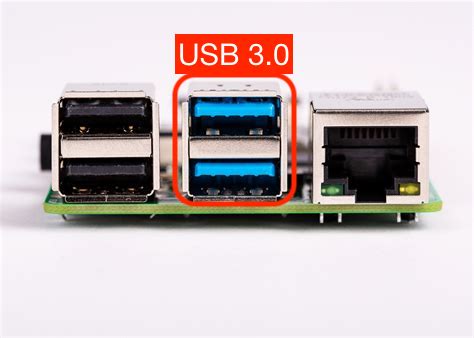
Insert the SSD into one of the blue usb3 ports. Then insert the HDMI, Keyboard, Mouse, Ethernet, and power supply.
caution
The first Pi4's to ship did not boot from USB3 by default, nowadays they do. If your image does not boot the two most common issues are older firmware on your Pi or an incompatible USB3 adaptor.
info
All we really need to do here is disable auto-login & create the ada user with sudo privileges. After we log back in we will delete the default Pi user and configure the server & environment for cardano-node & cardano-cli.
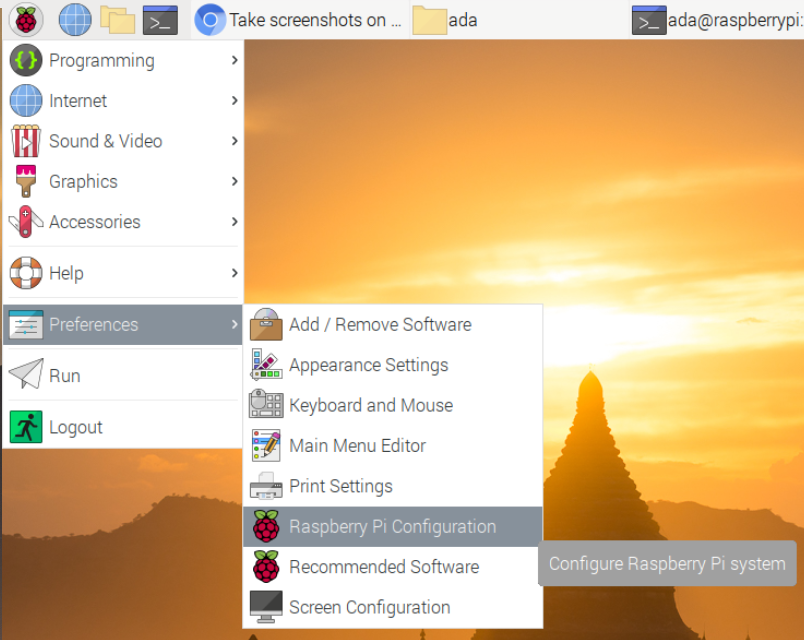
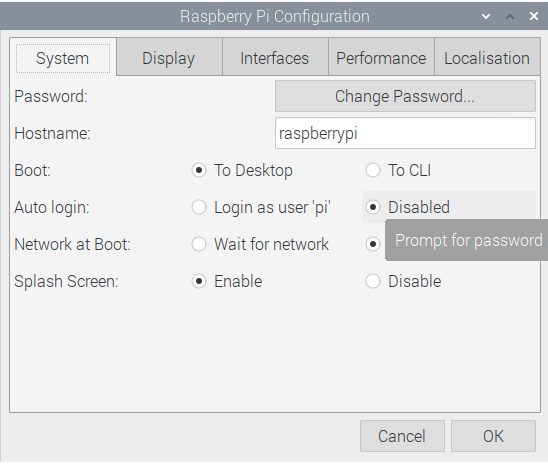
Create the ada user
This guide strives to be user agnostic so you can choose a different username and you should be ok. When creating the systemd services however you will have to edit the user. Pay attention!
Open a terminal then create a new user and add it to the sudo group.
sudo adduser ada; sudo adduser ada sudo
Update Raspbery Pi OS and reboot the server to make sure you are on the latest kernel. Reboot and log in as your new user.
sudo apt update; sudo apt upgrade
Change password
You can change the users password at anytime with the following command.
passwd
caution
Careful where you use sudo. For example issuing 'sudo passwd' would change the root password. This seems to be a place where new users get confused.
Delete the pi user
The pi user is set to auto login and does not require a password for sudo commands. Best to just trash it to avoid any potential security issues.
sudo deluser --remove-home pi
Server setup
Configure Hardware
Let's save some power, raise the governor on the CPU a bit, and set GPU ram as low as we can.
Here are some links for overclocking and testing your drive speeds. If you have heat sinks you can safely go to 2000. Just pay attention to over volt recommendations to go with your chosen clock speed.
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/config-txt/overclocking.md
- https://www.seeedstudio.com/blog/2020/02/12/how-to-safely-overclock-your-raspberry-pi-4-to-2-147ghz/
- https://www.tomshardware.com/how-to/raspberry-pi-4-23-ghz-overclock
- https://dopedesi.com/2020/11/24/upgrade-your-raspberry-pi-4-with-a-nvme-boot-drive-by-alex-ellis-nov-2020/
- Legendary Technology: New Raspberry Pi 4 Bootloader USB
Overclock, memory & radios
Edit /boot/config.txt.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Just paste the Pi Pool additions in at the bottom.
## Pi Pool ##
over_voltage=6
arm_freq=2000
use CTRL + x to save and y to confirm and exit.
Save and reboot.
sudo reboot
Configure Raspbian
Disable the root user
sudo passwd -l root
Secure shared memory
Mount shared memory as read only. Open /etc/fstab.
sudo nano /etc/fstab
Add this line at the bottom, save & exit.
tmpfs /run/shm tmpfs ro,noexec,nosuid 0 0
Increase open file limit for $USER
Add a couple lines to the bottom of /etc/security/limits.conf
sudo bash -c "echo -e '${USER} soft nofile 800000\n${USER} hard nofile 1048576\n' >> /etc/security/limits.conf"
Confirm it was added to the bottom.
cat /etc/security/limits.conf
Optimize performance & security
caution
If you would like to disable ipv6 or turn on forwarding you can below.
Add the following to the bottom of /etc/sysctl.conf. Save and exit.
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
## Pi Node ##
fs.file-max = 10000000
fs.nr_open = 10000000
# enable forwarding if using wireguard
net.ipv4.ip_forward=0
# ignore ICMP redirects
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses = 1
# disable IPv6
#net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
#net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
# block SYN attacks
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 2048
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 3
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_recv=45
# in progress tasks
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 240
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 4
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 5
# reboot if we run out of memory
vm.panic_on_oom = 1
kernel.panic = 10
# Use Google's congestion control algorithm
net.core.default_qdisc = fq
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbr
Load our changes after boot
Create a new file. Paste, save & close.
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
#
# rc.local
#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
# bits.
#
# By default this script does nothing.
# Print the IP address
_IP=$(hostname -I) || true
if [ "$_IP" ]; then
printf "My IP address is %s\n" "$_IP"
fi
# Give CPU startup routines time to settle.
sleep 120
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
exit 0
Chrony
We need to get our time synchronization as accurate as possible. Open /etc/chrony/chrony.conf
sudo apt install chrony
sudo nano /etc/chrony/chrony.conf
Replace the contents of the file with below, Save and exit.
pool time.google.com iburst minpoll 2 maxpoll 2 maxsources 3 maxdelay 0.3
pool time.euro.apple.com iburst minpoll 2 maxpoll 2 maxsources 3 maxdelay 0.3
pool time.apple.com iburst minpoll 2 maxpoll 2 maxsources 3 maxdelay 0.3
pool ntp.ubuntu.com iburst minpoll 2 maxpoll 2 maxsources 3 maxdelay 0.3
# This directive specify the location of the file containing ID/key pairs for
# NTP authentication.
keyfile /etc/chrony/chrony.keys
# This directive specify the file into which chronyd will store the rate
# information.
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
# Uncomment the following line to turn logging on.
#log tracking measurements statistics
# Log files location.
logdir /var/log/chrony
# Stop bad estimates upsetting machine clock.
maxupdateskew 5.0
# This directive enables kernel synchronisation (every 11 minutes) of the
# real-time clock. Note that it can’t be used along with the 'rtcfile' directive.
rtcsync
# Step the system clock instead of slewing it if the adjustment is larger than
# one second, but only in the first three clock updates.
makestep 0.1 -1
# Get TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system tz database
leapsectz right/UTC
# Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source.
local stratum 10
Save & exit.
sudo service chrony restart
Zram swap
info
We have found that cardano-node can safely use this compressed swap in ram essentially giving us around 20gb of ram. We already set kernel parameters for zram in /etc/sysctl.conf
Swapping to disk is slow, swapping to compressed ram space is faster and gives us some overhead before out of memory (oom).
Disable Raspbian swapfile.
sudo systemctl disable dphys-swapfile.service
sudo apt install zram-tools
sudo nano /etc/default/zramswap
# Compression algorithm selection
# speed: lz4 > zstd > lzo
# compression: zstd > lzo > lz4
# This is not inclusive of all that is available in latest kernels
# See /sys/block/zram0/comp_algorithm (when zram module is loaded) to see
# what is currently set and available for your kernel[1]
# [1] https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/Documentation/blockdev/zram.txt#L86
#ALGO=lz4
# Specifies the amount of RAM that should be used for zram
# based on a percentage the total amount of available memory
# This takes precedence and overrides SIZE below
PERCENT=150
# Specifies a static amount of RAM that should be used for
# the ZRAM devices, this is in MiB
#SIZE=256
# Specifies the priority for the swap devices, see swapon(2)
# for more details. Higher number = higher priority
# This should probably be higher than hdd/ssd swaps.
#PRIORITY=100
Save and reboot.
sudo reboot
Install packages
Install the packages we will need.
sudo apt install build-essential libssl-dev tcptraceroute python3-pip \
make automake unzip net-tools nginx ssl-cert pkg-config jq \
libffi-dev libgmp-dev libssl-dev libtinfo-dev libsystemd-dev \
zlib1g-dev g++ libncursesw5 libtool autoconf unattended-upgrades -y
sudo reboot
Automatic security updates
Enable automatic security updates.
sudo dpkg-reconfigure -plow unattended-upgrades
Environment Setup
description: Configure the environment for Cardano Node
Choose testnet or mainnet.
danger
There is a 500 ₳ Registration deposit and another 5 ₳ in registration costs to start a pool on mainnet. First time users are strongly reccomended to use testnet. You can get tada (test ada) from the testnet faucet. tada faucet link
Create the directories for our project.
mkdir -p ${HOME}/.local/bin
mkdir -p ${HOME}/pi-pool/files
mkdir -p ${HOME}/pi-pool/scripts
mkdir -p ${HOME}/pi-pool/logs
mkdir ${HOME}/git
mkdir ${HOME}/tmp
Create an .adaenv file, choose which network you want to be on and source the file. This file will hold the variables/settings for operating a Pi-Node. /home/ada/.adaenv
echo -e NODE_CONFIG=testnet >> ${HOME}/.adaenv; source ${HOME}/.adaenv
Create bash variables & add ~/.local/bin to our $PATH 🏃
caution
You must reload environment files after updating them. Same goes for cardano-node, changes to the topology or config files require a cardano-service restart.
echo . ~/.adaenv >> ${HOME}/.bashrc
cd .local/bin; echo "export PATH=\"$PWD:\$PATH\"" >> $HOME/.adaenv
echo export NODE_HOME=${HOME}/pi-pool >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export NODE_PORT=3003 >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export NODE_FILES=${HOME}/pi-pool/files >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export TOPOLOGY='${NODE_FILES}'/'${NODE_CONFIG}'-topology.json >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export DB_PATH='${NODE_HOME}'/db >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export CONFIG='${NODE_FILES}'/'${NODE_CONFIG}'-config.json >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export NODE_BUILD_NUM=$(curl https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/iohk-nix/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/index.html | grep -e "build" | sed 's/.*build\/\([0-9]*\)\/download.*/\1/g') >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
echo export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH="${HOME}/pi-pool/db/socket" >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
source ${HOME}/.bashrc; source ${HOME}/.adaenv
Build Libsodium
This is IOHK's fork of Libsodium. It is needed for the dynamic build binary of cardano-node.
cd; cd git/
git clone https://github.com/input-output-hk/libsodium
cd libsodium
git checkout 66f017f1
./autogen.sh
./configure
make
sudo make install
Echo library paths .bashrc file and source it.
echo "export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/local/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "export PKG_CONFIG_PATH="/usr/local/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH"" >> ~/.bashrc
. ~/.bashrc
Update link cache for shared libraries and confirm.
sudo ldconfig; ldconfig -p | grep libsodium
Retrieve node files
cd $NODE_FILES
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-byron-genesis.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-shelley-genesis.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-alonzo-genesis.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-topology.json
wget -N https://raw.githubusercontent.com/input-output-hk/cardano-node/master/cardano-submit-api/config/tx-submit-mainnet-config.yaml
Run the following to modify ${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json and update TraceBlockFetchDecisions to "true" & listen on all interfaces with Prometheus Node Exporter.
sed -i ${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json \
-e "s/TraceBlockFetchDecisions\": false/TraceBlockFetchDecisions\": true/g" \
-e "s/127.0.0.1/0.0.0.0/g"
info
Tip for relay nodes: It's possible to reduce memory and cpu usage by setting "TraceMemPool" to "false" in {NODE_CONFIG}-config.json. This will turn off mempool data in Grafana and gLiveView.sh.
Retrieve aarch64 1.33.1 and cardano-submit-api binaries
info
The unofficial cardano-node, cardano-cli and cardano-submit-api binaries available to us are being built by an IOHK engineer in his spare time. Consider delegating to zw3rk pool to support mobile Haskel development.
cd ${HOME}/tmp
wget https://ci.zw3rk.com/build/430108/download/1/aarch64-unknown-linux-musl-cardano-node-1.33.1.zip
unzip *.zip
mv cardano-node/cardano-* ${HOME}/.local/bin
rm -r *
cd ${HOME}
caution
If binaries already exist (if updating) you will have to confirm overwriting the old ones.
Confirm binaries are in $USER's $PATH.
cardano-node version
cardano-cli version
which cardano-submit-api
Systemd unit startup scripts
Create the systemd unit file and startup script so systemd can manage cardano-node.
nano ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-service
Paste the following, save & exit.
#!/bin/bash
. /home/ada/.adaenv
## +RTS -N4 -RTS = Multicore(4)
cardano-node run +RTS -N4 -RTS \
--topology ${TOPOLOGY} \
--database-path ${DB_PATH} \
--socket-path ${CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH} \
--port ${NODE_PORT} \
--config ${CONFIG}
Allow execution of our new cardano-node service file.
chmod +x ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-service
Open /etc/systemd/system/cardano-node.service.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/cardano-node.service
Paste the following, You will need to edit the username here if you chose to not use ada. Save & exit.
# The Cardano Node Service (part of systemd)
# file: /etc/systemd/system/cardano-node.service
[Unit]
Description = Cardano node service
Wants = network-online.target
After = network-online.target
[Service]
User = ada
Type = simple
WorkingDirectory= /home/ada/pi-pool
ExecStart = /bin/bash -c "PATH=/home/ada/.local/bin:$PATH exec /home/ada/.local/bin/cardano-service"
KillSignal=SIGINT
RestartKillSignal=SIGINT
TimeoutStopSec=10
LimitNOFILE=32768
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
EnvironmentFile=-/home/ada/.adaenv
[Install]
WantedBy= multi-user.target
Create the systemd unit file and startup script so systemd can manage cardano-submit-api.
nano ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-submit-service
#!/bin/bash
. /home/ada/.adaenv
cardano-submit-api \
--socket-path ${CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH} \
--port 8090 \
--config /home/ada/pi-pool/files/tx-submit-mainnet-config.yaml \
--listen-address 0.0.0.0 \
--mainnet
Allow execution of our new cardano-submit-api service script.
chmod +x ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-submit-service
Create /etc/systemd/system/cardano-submit.service.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/cardano-submit.service
Paste the following, You will need to edit the username here if you chose to not use ada. save & exit.
# The Cardano Submit Service (part of systemd)
# file: /etc/systemd/system/cardano-submit.service
[Unit]
Description = Cardano submit service
Wants = network-online.target
After = network-online.target
[Service]
User = ada
Type = simple
WorkingDirectory= /home/ada/pi-pool
ExecStart = /bin/bash -c "PATH=/home/ada/.local/bin:$PATH exec /home/ada/.local/bin/cardano-submit-service"
KillSignal=SIGINT
RestartKillSignal=SIGINT
TimeoutStopSec=10
LimitNOFILE=32768
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
EnvironmentFile=-/home/ada/.adaenv
[Install]
WantedBy= multi-user.target
Reload systemd so it picks up our new service files.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Let's add a couple functions to the bottom of our .adaenv file to make life a little easier.
nano ${HOME}/.adaenv
cardano-service() {
#do things with parameters like $1 such as
sudo systemctl "$1" cardano-node.service
}
cardano-submit() {
#do things with parameters like $1 such as
sudo systemctl "$1" cardano-submit.service
}
Save & exit.
source ${HOME}/.adaenv
What we just did there was add a couple functions to control our cardano-service and cardano-submit without having to type out
sudo systemctl enable cardano-node.service
sudo systemctl start cardano-node.service
sudo systemctl stop cardano-node.service
sudo systemctl status cardano-node.service
Now we just have to:
- cardano-service enable (enables cardano-node.service auto start at boot)
- cardano-service start (starts cardano-node.service)
- cardano-service stop (stops cardano-node.service)
- cardano-service status (shows the status of cardano-node.service)
Or
- cardano-submit enable (enables cardano-submit.service auto start at boot)
- cardano-submit start (starts cardano-submit.service)
- cardano-submit stop (stops cardano-submit.service)
- cardano-submit status (shows the status of cardano-submit.service)
The submit service listens on port 8090. You can connect your Nami wallet like below to submit tx's yourself in Nami's settings.
http://<node lan ip>:8090/api/submit/tx
⛓ Syncing the chain ⛓
You are now ready to start cardano-node. Doing so will start the process of 'syncing the chain'. This is going to take about 48 hours and the db folder is about 13GB in size right now. We used to have to sync it to one node and copy it from that node to our new ones to save time. However...
Download snapshot
I have started taking snapshots of my backup nodes db folder and hosting it in a web directory. With this service it takes around 20 minutes to pull the latest snapshot and maybe another hour to sync up to the tip of the chain. This service is provided as is. It is up to you. If you want to sync the chain on your own simply:
cardano-service enable
cardano-service start
cardano-service status
Otherwise, be sure your node is not running & delete the db folder if it exists and download db/.
cardano-service stop
cd $NODE_HOME
rm -r db/
Download Database
wget -r -np -nH -R "index.html*" -e robots=off https://$NODE_CONFIG.adamantium.online/db/
Once wget completes enable & start cardano-node.
cardano-service enable
cardano-service start
cardano-service status
gLiveView.sh
Guild operators scripts has a couple useful tools for operating a pool. We do not want the project as a whole, though there are a couple scripts we are going to use.
Guild Operators Helper Scripts
cd $NODE_HOME/scripts
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cardano-community/guild-operators/master/scripts/cnode-helper-scripts/env
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cardano-community/guild-operators/master/scripts/cnode-helper-scripts/gLiveView.sh
info
You can change the port cardano-node runs on in the .adaenv file in your home directory. Open the file edit the port number. Load the change into your shell & restart the cardano-node service.
nano /home/ada/.adaenv
source /home/ada/.adaenv
cardano-service restart
Add a line sourcing our .adaenv file to the top of the env file and adjust some paths.
sed -i env \
-e "/#CNODEBIN/i. ${HOME}/.adaenv" \
-e "s/\#CNODE_HOME=\"\/opt\/cardano\/cnode\"/CNODE_HOME=\"\${HOME}\/pi-pool\"/g" \
-e "s/\#CNODE_PORT=6000"/CNODE_PORT=\"'${NODE_PORT}'\""/g" \
-e "s/\#CONFIG=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/files\/config.json\"/CONFIG=\"\${NODE_FILES}\/"'${NODE_CONFIG}'"-config.json\"/g" \
-e "s/\#TOPOLOGY=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/files\/topology.json\"/TOPOLOGY=\"\${NODE_FILES}\/"'${NODE_CONFIG}'"-topology.json\"/g" \
-e "s/\#LOG_DIR=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/logs\"/LOG_DIR=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/logs\"/g"
Allow execution of gLiveView.sh.
chmod +x gLiveView.sh
topologyUpdater.sh
Until peer to peer is enabled on the network operators need a way to get a list of relays/peers to connect to. The topology updater service runs in the background with cron. Every hour the script will run and tell the service you are a relay and want to be a part of the network. It will add your relay to it's directory after four hours you should see in connections in gLiveView.
info
The list generated will show you the distance & a clue as to where the relay is located.
Download the topologyUpdater script and have a look at it. Lower the number of peers to 10 and add any custom peers you wish. These are outgoing connections. You will not see any incoming transactions untill other nodes start connecting to you.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cardano-community/guild-operators/master/scripts/cnode-helper-scripts/topologyUpdater.sh
Lower the number of MX_PEERS to 10.
nano topologyUpdater.sh
Save, exit and make it executable.
chmod +x topologyUpdater.sh
caution
You will not be able to successfully execute ./topologyUpdater.sh until you are fully synced up to the tip of the chain.
Create a cron job that will run the script every hour.
crontab -e
info
Choose nano when prompted for editor.
Add the following to the bottom, save & exit.
info
The Pi-Node image has this cron entry disabled by default. You can enable it by removing the #.
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/home/ada/.local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin
33 * * * * . $HOME/.adaenv; $HOME/pi-pool/scripts/topologyUpdater.sh
After four hours you can open ${NODE_CONFIG}-topology.json and inspect the list of out peers the service suggested for you. Remove anything more than 7k distance(or less). IOHK recently suggested 8 out peers. The more out peers the more system resources it uses. You can also add any peers you wish to connect to manualy inside the script. This is where you would add your block producer or any friends nodes.
nano $NODE_FILES/${NODE_CONFIG}-topology.json
info
You can use gLiveView.sh to view ping times in relation to the peers in your {NODE_CONFIG}-topology file. Use Ping to resolve hostnames to IP's.
Changes to this file will take affect upon restarting the cardano-service.
caution
Don't forget to remove the last comma in your topology file!
Status should show as enabled & running.
Once your node syncs past epoch 208(shelley era) you can use gLiveView.sh to monitor your sync progress.
danger
It can take over an hour for cardano-node to sync to the tip of the chain. Use ./gliveView.sh, htop and log outputs to view process. Be patient it will come up.
cd $NODE_HOME/scripts
./gLiveView.sh
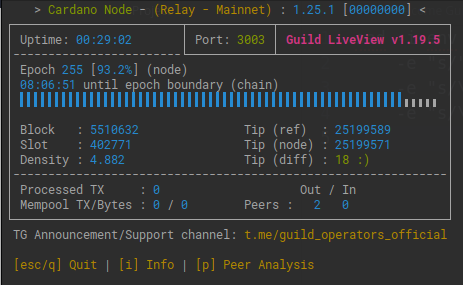
Prometheus, Node Exporter & Grafana
Prometheus connects to cardano-nodes backend and serves metrics over http. Grafana in turn can use that data to display graphs and create alerts. Our Grafana dashboard will be made up of data from our Ubuntu system & cardano-node. Grafana can display data from other sources as well, like adapools.org.
info
You can connect a Telegram bot to Grafana which can alert you of problems with the server. Much easier than trying to configure email alerts.
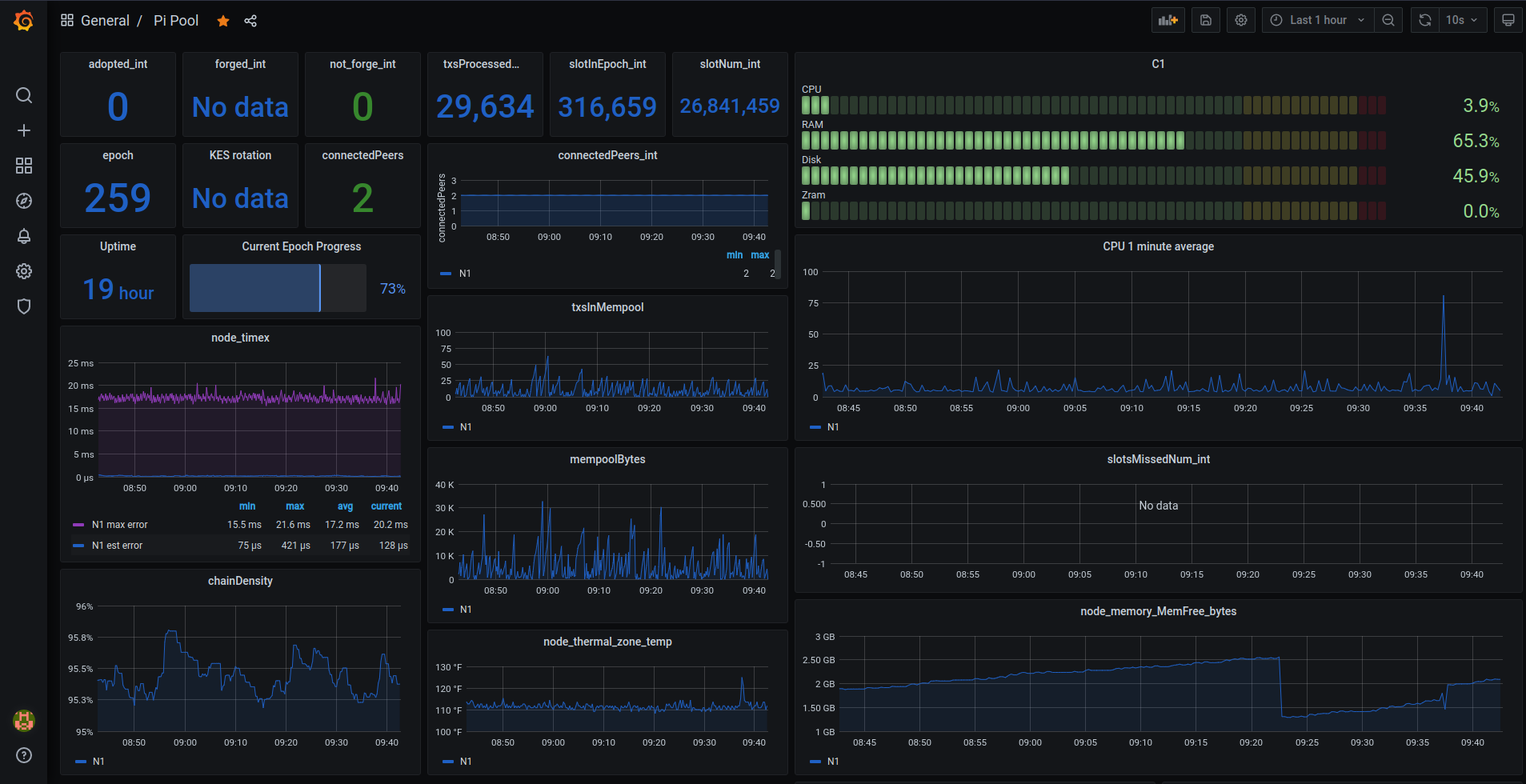
Install Prometheus & Node Exporter.
info
Prometheus can scrape the http endpoints of other servers running node exporter. Meaning Grafana and Prometheus does not have to be installed on your core and relays. Only the package prometheus-node-exporter is required if you would like to build a central Grafana dashboard for the pool, freeing up resources and having a single dashboard to monitor everything.
sudo apt install prometheus prometheus-node-exporter -y
Disable them in systemd for now.
sudo systemctl disable prometheus.service
sudo systemctl disable prometheus-node-exporter.service
Configure Prometheus
Open prometheus.yml.
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Replace the contents of the file with.
caution
Indentation must be correct YAML format or Prometheus will fail to start.
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # By default, scrape targets every 15 seconds.
# Attach these labels to any time series or alerts when communicating with
# external systems (federation, remote storage, Alertmanager).
external_labels:
monitor: "codelab-monitor"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label job=<job_name> to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "Prometheus" # To scrape data from Prometheus Node Exporter
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
# - targets: ['<CORE PRIVATE IP>:12798']
# labels:
# alias: 'C1'
# type: 'cardano-node'
# - targets: ['<RELAY PRIVATE IP>:12798']
# labels:
# alias: 'R1'
# type: 'cardano-node'
- targets: ["localhost:12798"]
labels:
alias: "N1"
type: "cardano-node"
# - targets: ['<CORE PRIVATE IP>:9100']
# labels:
# alias: 'C1'
# type: 'node'
# - targets: ['<RELAY PRIVATE IP>:9100']
# labels:
# alias: 'R1'
# type: 'node'
- targets: ["localhost:9100"]
labels:
alias: "N1"
type: "node"
Save & exit.
Start Prometheus.
sudo systemctl start prometheus.service
Install Grafana
Add Grafana's gpg key to Ubuntu.
wget -q -O - https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
Add latest stable repo to apt sources.
echo "deb https://packages.grafana.com/oss/deb stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list
Update your package lists & install Grafana.
sudo apt update; sudo apt install grafana
Change the port Grafana listens on so it does not clash with cardano-node.
sudo sed -i /etc/grafana/grafana.ini \
-e "s#;http_port#http_port#" \
-e "s#3000#5000#"
Start Grafana
sudo systemctl start grafana-server.service
cardano-monitor bash function
Open .adaenv.
cd ${HOME}; nano .adaenv
Down at the bottom add.
cardano-monitor() {
#do things with parameters like $1 such as
sudo systemctl "$1" prometheus.service
sudo systemctl "$1" prometheus-node-exporter.service
sudo systemctl "$1" grafana-server.service
}
Save, exit & source.
source .adaenv
Here we tied all three services under one function. Enable Prometheus.service, prometheus-node-exporter.service & grafana-server.service to run on boot and start the services.
cardano-monitor enable
cardano-monitor start
caution
At this point you may want to start cardano-service and get synced up before we continue to configure Grafana. Go to the syncing the chain section. Choose whether you want to wait 30 hours or download the latest chain snapshot. Return here once gLiveView.sh shows you are at the tip of the chain.
Grafana, Nginx proxy_pass & snakeoil
Let's put Grafana behind Nginx with self signed(snakeoil) certificate. The certificate was generated when we installed the ssl-cert package.
You will get a warning from your browser. This is because ca-certificates cannot follow a trust chain to a trusted (centralized) source. The connection is however encrypted and will protect your passwords flying around in plain text.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
Replace contents of the file with below.
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
# SSL configuration
#
listen 443 ssl default_server;
#listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don't use them in a production server!
#
include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
add_header X-Proxy-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5000;
proxy_redirect off;
include proxy_params;
}
}
Check that Nginx is happy with our changes and restart it.
sudo nginx -t
## if ok, do
sudo service nginx restart
You can now visit your pi-nodes ip address without any port specification, the connection will be upgraded to SSL/TLS and you will get a scary message(not really scary at all). Continue through to your dashboard.
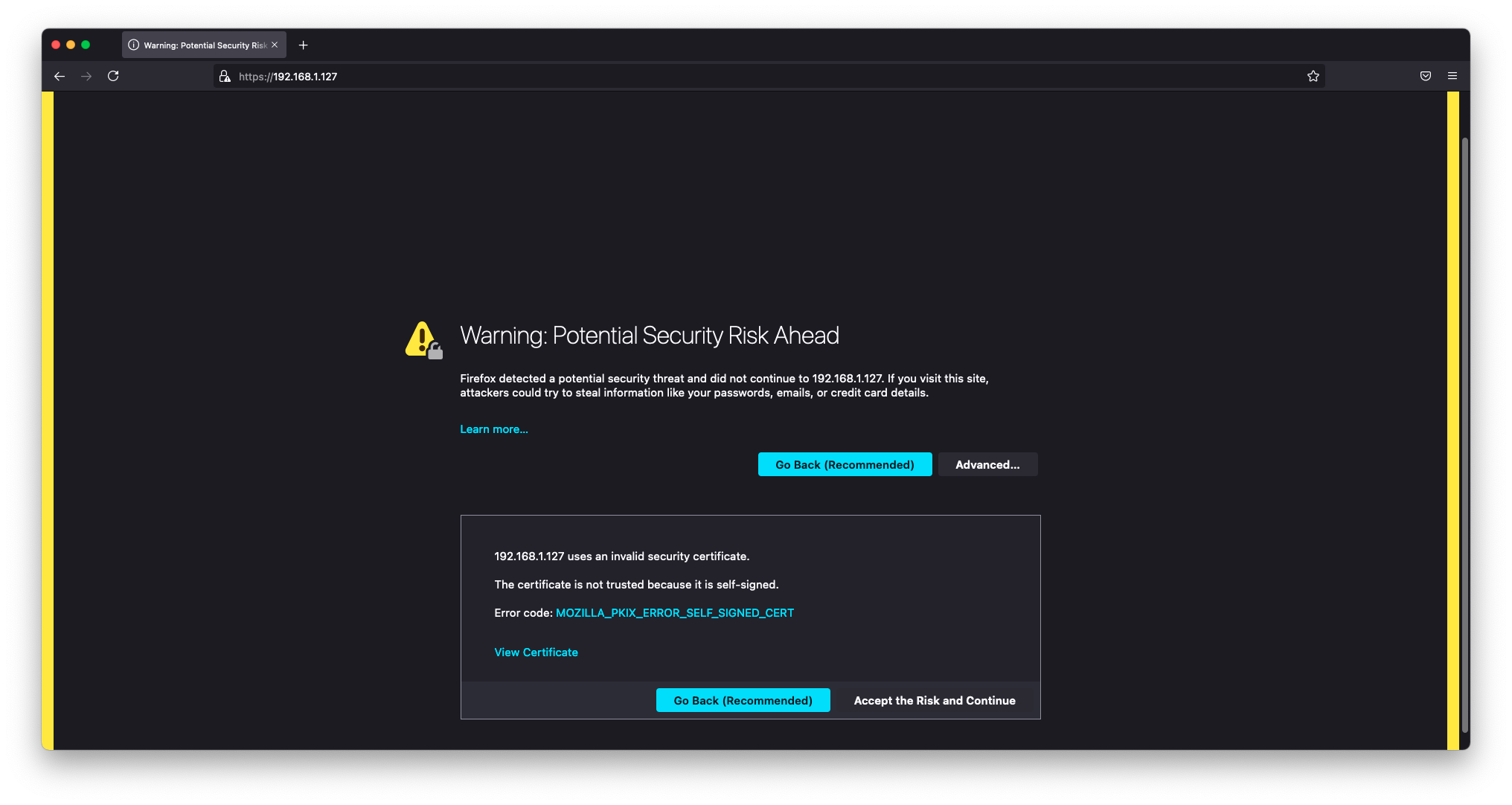
Configure Grafana
On your local machine open your browser and enter your nodes private ip address.
Log in and set a new password. Default username and password is admin:admin.
Configure data source
In the left hand vertical menu go to Configure > Datasources and click to Add data source. Choose Prometheus. Enter http://localhost:9090 where it is grayed out, everything else can be left default. At the bottom save & test. You should get the green "Data source is working" if cardano-monitor has been started. If for some reason those services failed to start issue cardano-service restart.
Import dashboards
Save the dashboard json files to your local machine.
Armada Alliance Grafana Dashboards
In the left hand vertical menu go to Dashboards > Manage and click on Import. Select the file you just downloaded/created and save. Head back to Dashboards > Manage and click on your new dashboard.

Configure poolDataLive
Here you can use the poolData api to bring extra pool data into Grafana like stake & price.
Follow the instructions to install the Grafana plugin, configure your datasource and import the dashboard.
sudo grafana-cli plugins install simpod-json-datasource
cardano-monitor restart
Useful Commands
info
View how much zram swap cardano-node is using.
CNZRAM=$(pidof cardano-node)
grep --color VmSwap /proc/$CNZRAM/status
Follow log output to journal.
sudo journalctl --unit=cardano-node --follow
Follow log output to stdout.
sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog
View network connections with netstat.
sudo netstat -puntw
From here you have a Pi-Node with tools to build an active relay or a stake pool from the following pages. Best of luck and please join the armada-alliance, together we are stronger! 💪